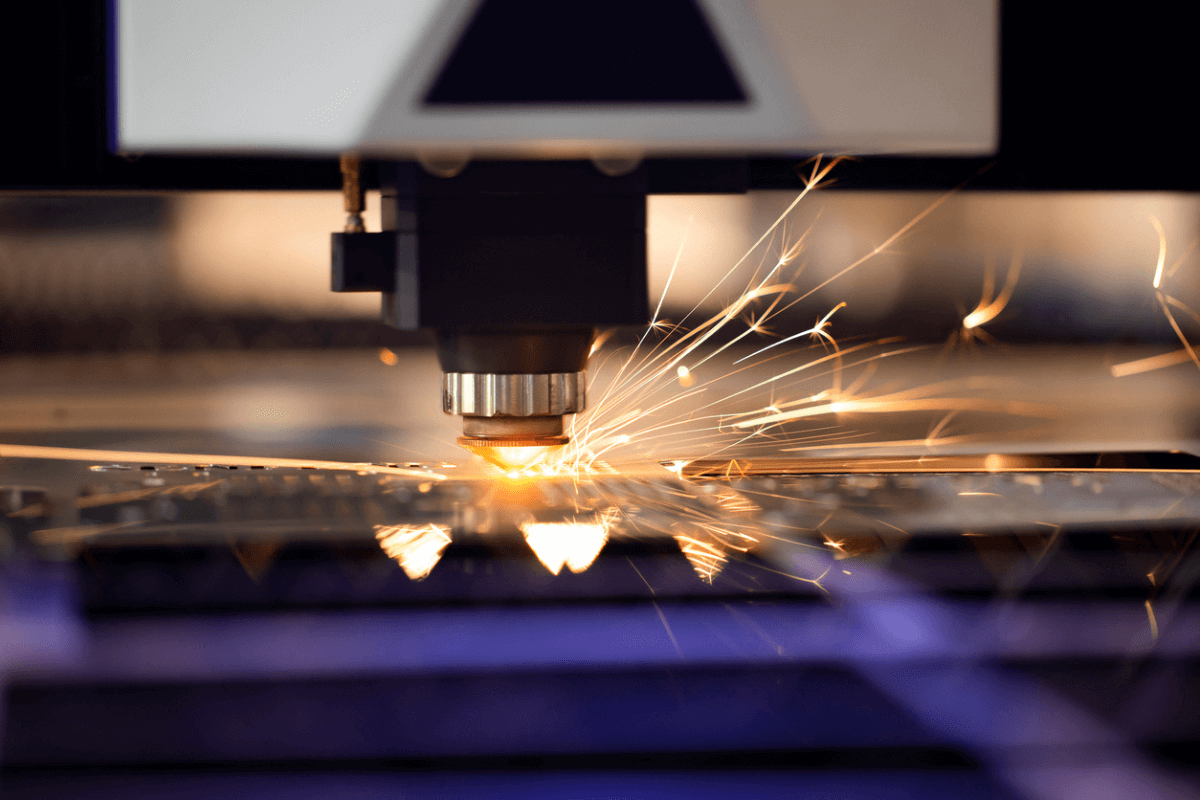
Are you looking for a way to enhance your laser cutting? For improved edges, faster cuts, and lower ongoing maintenance costs, you need to select the right assist gas.
In this article, we explore the various options for assist gases for laser cutting and the advantages each provides. Read on to learn how the right assist gas could improve your efficiency and work output.
How does laser cutting work?
A laser-cutting machine works by aiming a high-powered laser beam at the material that needs to be cut. The beam generates intense heat in a focused location, melting the material along its path. An assist gas, such as nitrogen or oxygen, is often used to blow away the melted material and improve the edge quality of the cut. The laser cutter's head is guided by computer-aided design (CAD) software to produce the desired shape.
The cutting speed and laser power can be adjusted based on the type and thickness of the material being cut, ensuring precise and accurate results.
Benefits of assist gas for laser cutting:
- High definition cuts
- Faster cutting speeds
- Protection for laser optics
- Reduced maintenance.
When choosing which assist gas to invest in, it's crucial to understand the different applications and advantages of each option.
The top assist gases for laser cutting
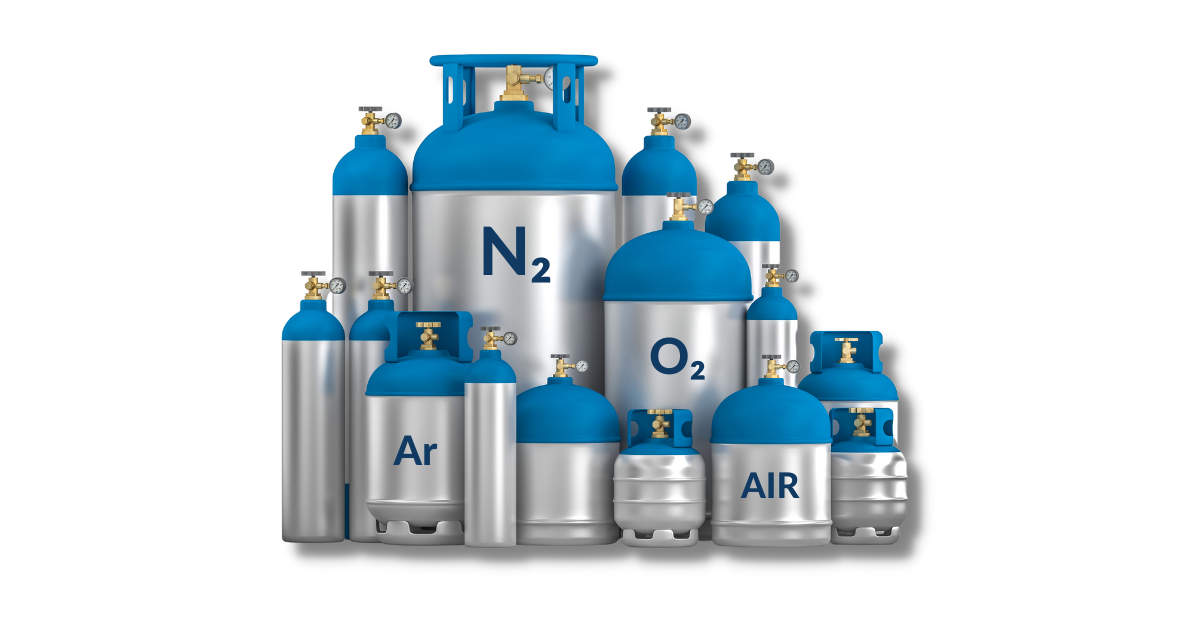

The two main options for assist gases are oxygen and nitrogen, though compressed air and argon are also viable options. Each gas offers a set of advantages and disadvantages, suited to particular applications.
Oxygen for laser cutting
Oxygen is the most common gas used for laser cutting mild and carbon steel. It is also known as the ‘cutting gas’. When the laser beam is active, the reaction between oxygen and the metal creates additional heat energy to support the cutting process. The liquid iron oxide is then removed from the cut through the sheer force of the oxygen jet.
To enhance the melt-shear removal process, oxygen pressure can be increased. However, higher oxygen concentrations can lead to increased side burning, causing poor cuts with more dross. In some cases, it may even result in failure to cut.
The maximum applicable oxygen pressure is determined by the material thickness. For thin sheets of 2-3mm, up to 20-bar of pressure can be used, where the melt-shear removal process is dominant. For thicker sheets over 20mm, the maximum oxygen pressure is rarely over 1-bar.
Benefits of oxygen for laser cutting
The benefits of using oxygen as an assist gas in laser cutting include:
- Edge quality
- Cutting speed
- Reduced dross
- Longer lifespan of laser optics
- Efficiency.
Laser cutting applications for oxygen
If you use a laser cutter for cutting mild and carbon steels, oxygen is likely the most effective assist gas. The reaction between oxygen and the metal will create additional heat energy to speed up the cutting process. If you work with materials that are sensitive to oxidisation, oxygen will not be a suitable solution.
Nitrogen for laser cutting
Another popular assist gas used for laser cutting, nitrogen is an inert gas, meaning it does not react with the material being cut. This results in reduced oxidation and discolouration, unlike with oxygen. Nitrogen also helps to blow away the melted material, leading to a cleaner and smoother cut.
Nitrogen also cools the material being cut which reduces warping and improves the accuracy of the final product. In addition, nitrogen acts as a protective shield, preventing molten material from splattering and damaging the laser optics. This extends the lifespan of the laser optics and reduces the frequency of maintenance.
Nitrogen can also be adjusted to optimise the cutting process for different materials and applications, making it a versatile choice for laser cutting.
Benefits of nitrogen for laser cutting
The benefits of using nitrogen as an assist gas in laser cutting include:
- Improved edge quality
- Reduced oxidation
- Reduced warping
- Longer lifespan of laser optics
- Efficient cutting.
Laser cutting applications for nitrogen
The most suitable metals for laser cutting with nitrogen include stainless steel, aluminium, copper and brass, non-ferrous metals, and high-alloy steels. Since nitrogen is an inert gas, it does not contribute to the reaction between the laser and the material being cut, making it suitable for a wide range of materials and applications.
Compressed air for laser cutting
Compressed air is a mixture of gases, including nitrogen and oxygen. This makes it a reactive cutting gas, but less so than oxygen. It is an easy and economical option to connect to an existing air setup and, if required, a pressure booster can be easily added. It is worth noting that a filter is needed to clean the air of impurities.
Benefits of compressed air for laser cutting
The benefits of using compressed air as an assist gas in laser cutting include:
- Cost-effective
- Can be added to an existing shop air setup
- Suitable for many metals
- High-quality cuts on aluminium
- Faster cuts on thin materials.
Laser cutting applications for compressed air
Compressed air is a cost-effective option, particularly for cutting aluminium, mild steel, and other thin metals. However, it is not suitable for certain reactive materials such as titanium, magnesium, and aluminium alloys. Additionally, if used without proper filtration, oil and moisture can contaminate the optics, leading to lower cutting quality and decreased machine lifespan.
Argon for laser cutting
Argon is also an inert gas but is less chemically reactive than nitrogen. It is a more expensive assist gas but is also known for producing high-quality cuts. Due to its higher price, argon is mostly used for cutting titanium and other metals that react to nitrogen.
Benefits of argon for laser cutting
The benefits of using argon as an assist gas in laser cutting include:
- Suitable for reactive metals
- High-quality cuts
- Removes heat from cuts faster than nitrogen
- Narrow heat-affected zone, ideal for certain steel formulations.
Laser cutting applications for argon
Argon is the preferred assist gas for laser cutting reactive metals like titanium, magnesium, and aluminium alloys. However, it may cause some materials, such as martensite steel, to have a slightly brittle edge. The added expense will also be a contributing factor.
Laser cutting NZ
At Industrial Air Systems, our laser cutting solutions are designed to optimise your efficiency and enhance your cut quality. Our most popular laser cutting systems include the Nitropak and the Airpak15 Air-Assist.
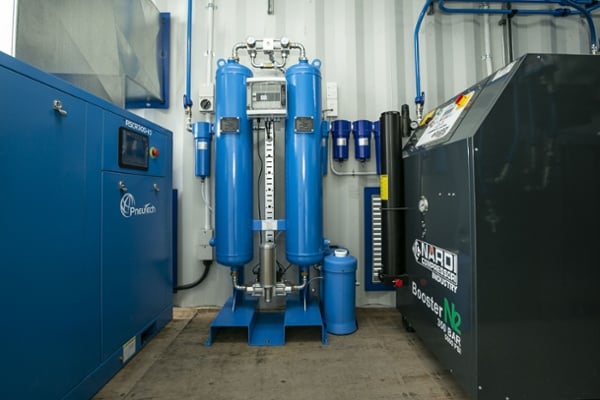
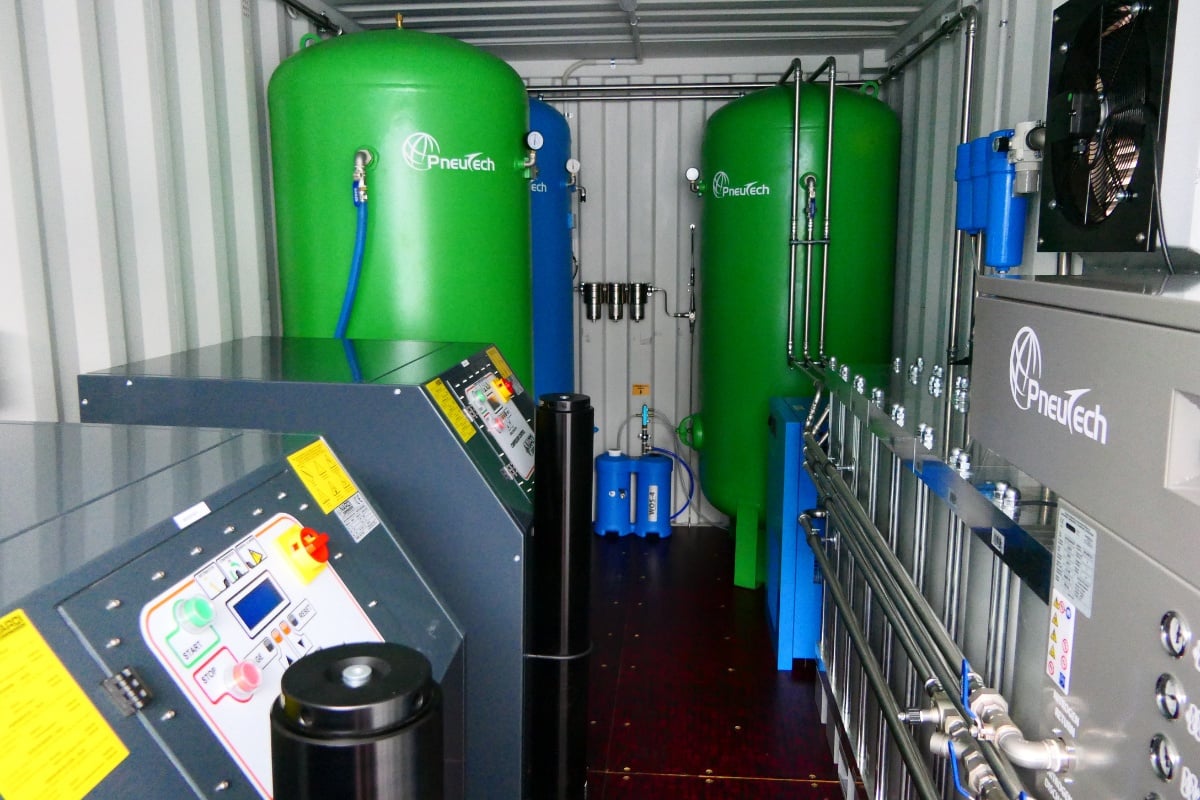
Nitropak Laser Cutting Nitrogen Generator
Designed for laser cutting applications, the Nitropak is a complete nitrogen generator system. For increased air purity, the Nitropak incorporates a 7-stage low and high-pressure filtration system to separate any oil contamination down to 0.01 microns. The Nitropak comes in a compact, containerised package, providing a pure and consistent nitrogen gas supply for your laser cutter.
Learn more about the Nitropak >
Airpak15 Air-assist Compressor
Also designed for laser cutting, the Airpak15 Air-Assist from PneuTech has an adsorption dryer that reduces compressed air to a dewpoint of below -40ºC. The carbon tower also eliminates residual oil vapours and ensures that no contamination enters the laser supply line.
Learn more about the Airpak15 air-assist >
For more advice and information, contact the team at Industrial Air Systems. We can recommend a suitable assist gas as well as various systems to improve your laser cutting operations. Or browse our wide range of laser cutting systems at the link below.







.jpg)