Managing a warehouse is a complex and multifaceted process, requiring a lot of careful planning and effective systems. To ensure you know all the expenses involved, we’ve outlined the key operational costs for warehouses in this article.
If you are looking for new equipment or need ways to cut down on running costs, this article is for you. Keep reading to find our industry advice and recommendations on how to increase your efficiency.
Warehouse operating costs
The operating costs of your warehouse will significantly impact your profitability and must be optimised to improve your bottom line. The most significant operating costs for most warehouses include the following:
- Labour
- Rent and utilities
- Equipment running costs
- Maintenance
Labour
The hours and energy your employees put in are a large portion of your ongoing costs. This includes any time invested in operating machines, repairs, manufacturing, cleaning, maintenance, and security.
To ensure your employees are operating at their highest level of productivity, you need to review your processes regularly and look for ways to optimise them. Common ways to do this include investing in more efficient equipment or training. The cost of labour will depend on the skills your employees have, contracting rates, and the total hours spent.
How to calculate the average monthly labour cost
- Add up the amount paid to each worker over one month (employees and contractors).
- Divide the result by the total hours worked in that month.
- At the end of the year, add these together and divide by twelve for the monthly average.
Rent and utilities
Another significant operating cost for warehouses is the regular cost of using the building and services, such as:
- Rent or rates
- Power
- Gas
- Water
To minimise these costs, we recommend investing in energy-efficient equipment and finding a warehouse that suits your operational needs. For example, if you opt for a warehouse with excess space, you may waste money heating and cooling areas you aren’t actually using.
Usually, rent is fairly consistent across each month but utilities can vary depending on your work output. For an average monthly rate, track the bill each month, total it, and divide it by twelve.
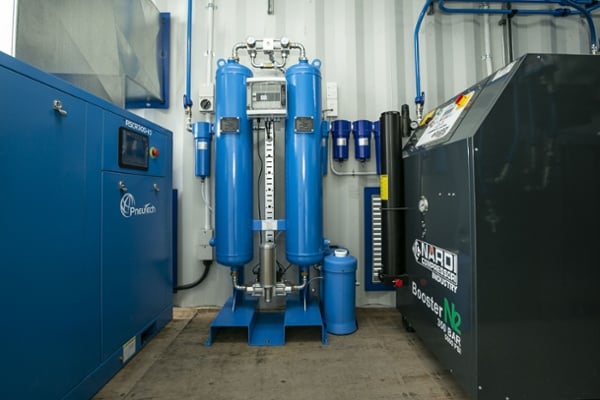
Equipment running costs
One of the biggest costs of industrial warehouses is the running cost of equipment, especially when used to manufacture or process products. Some common examples of industrial equipment include:
- Manufacturing machinery
- Handling equipment
- Power generators
- Air compressors and pumps
- Industrial automation systems
- Air conditioning
- Testing and measurement equipment
- Safety equipment
How to calculate your equipment running costs
Depending on the amount of equipment and the amount of time each tool is used, energy consumption can add up to a very large expense. To calculate the average energy consumption, and cost of your warehouse equipment, you’ll need to track the amount of power used each month. To keep your costs as low as possible, make sure each piece of equipment is the right fit for the tasks it performs.
For example, the cost of running an air compressor is highly dependent on how energy efficient the compressor is and the size compared to the intended application. If your air compressor is oversized, it will use far more energy and will cost more to run. On the other hand, a correctly sized compressor that only produces air when needed will give you the exact amount of air required for the task at hand, without wasting power.
Maintenance
As with any equipment or tools, expect to pay a certain amount toward upkeep and repairs. This will include one-off fixes, regular servicing, and replacements, which can amount to a significant total cost.
To ensure your equipment is running at optimal capacity, you need to:
- Follow manufacturer guidelines
- Establish a regular servicing program
- Keep equipment clean
- Train machine operators.
While these steps will incur some costs, they will also help to reduce unexpected breakdowns and downtime, keeping your warehouse operational for longer periods of time. Besides saving you money over time, this will also extend the equipment's lifespan and ensure employee safety.
How to reduce your operating costs

One of the most effective ways to reduce your operating costs is to focus on energy efficiency. Here are our top five ways to reduce your energy consumption:
1. Insulation
When heating and cooling a large industrial building, air conditioning can be a huge expense. To maintain comfortable working conditions all year round, insulating your workspaces may be a wise investment. This is particularly true for warehouses that process food products, which need to be stored or manufactured within a certain temperature range.
2. Automated lighting
Lighting is another critical overhead so start by using energy-efficient light bulbs that draw less power. Additionally, don’t leave lights on after business hours and fit sensors in offices, meeting rooms, and workshop spaces. These small actions cut down your energy bill quickly, with minimal effort from you or your employees.
3. Off-grid power
Consider setting up an off-grid power system to escape the monopoly of an energy provider. Transitioning to renewable energy can provide both cost savings and a reduced carbon footprint. When considering solar power, assess your energy usage patterns to determine the return on investment.
4. Efficient equipment
Review your company’s equipment and see how much energy could be saved by moving to updated, energy-efficient designs. With so many pieces of equipment drawing power, opting for models with low-power modes and automatic standby can greatly reduce your energy consumption in a busy warehouse.
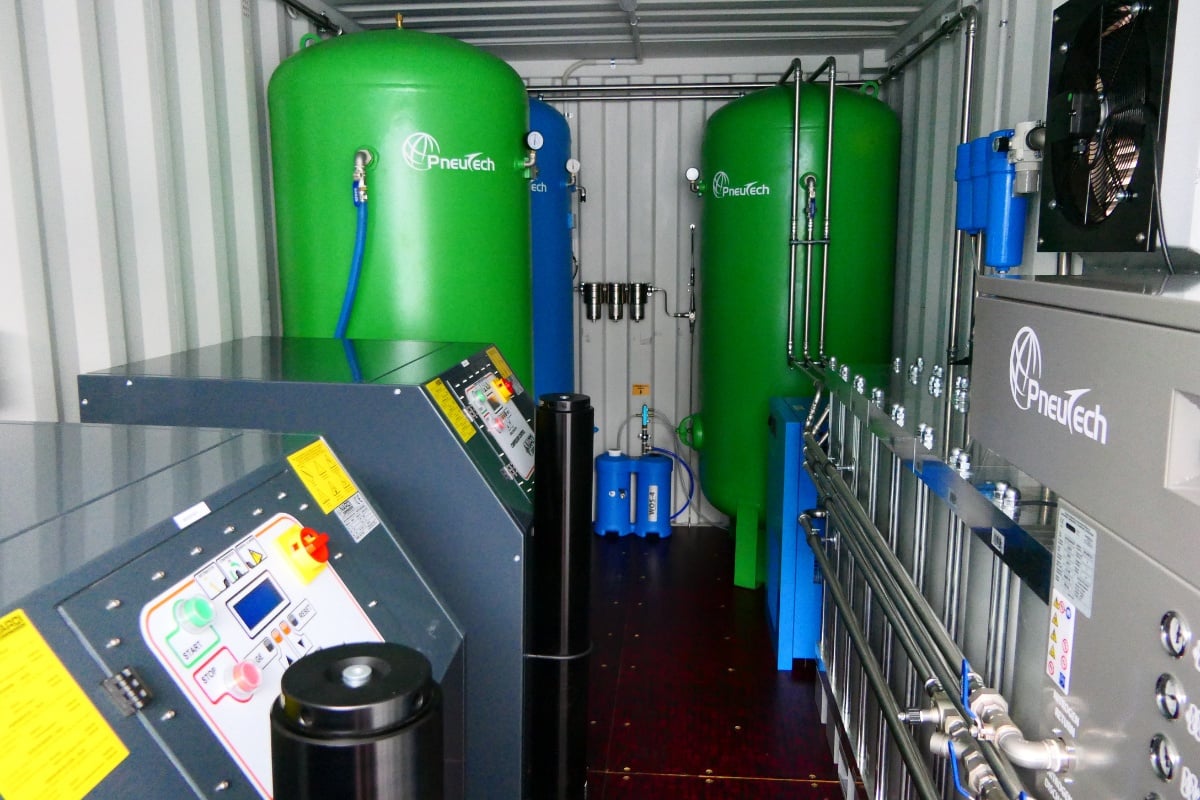
Efficient air compressors
One crucial thing to consider is your air compressor costs, as this can be a large operating expense. Here are 3 tips on how to reduce yours:
Variable-speed air compressors

Fixed-speed compressors run at a constant speed, while variable-speed compressors adjust their output based on demand, allowing for more efficiency. They match the air demand to the application, which reduces wasted energy by avoiding constant high-speed operation. Although they do come at a higher upfront cost than fixed-speed compressors, variable-speed compressors are far more energy-efficient and have longer lifespans.
Multiple air compressors
Having multiple different air compressors for different jobs ensures that your compressed air system is running as efficiently as possible. For example, you may choose a fixed-speed compressor for a base supply of air and a variable-speed compressor to meet peaks in demand.
Air receivers
If you operate a business like a winery that only uses large amounts of compressed air at certain times of the year, then purchasing a big air compressor will be a waste during months when it will get little use. By adding storage like air receivers to your compressed air system, you can manage your compressed air supply to suit demand.
Running a warehouse comes with significant operating costs, including labour, rent, utilities, and equipment. To minimise these costs, invest in energy-efficient equipment that is designed to use less energy while delivering the same high-quality performance.
Contact us for advice tailored to your industry and warehouse output. We will help you find the right compressed air equipment for your needs, maximising productivity and minimising running costs. Or, download our ultimate guide to air compressors, featuring everything you need to know about optimising your system.






.jpg)